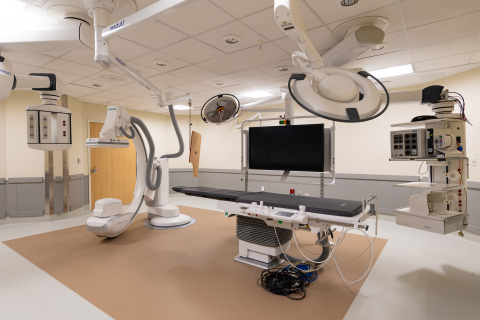
In many cases, balloon catheters are used by physician in cath lab. A catheterization laboratory, commonly referred to as a cath lab, is an examination room in a hospital or clinic with diagnostic imaging equipment used to visualize the arteries of the heart and the chambers of the heart and treat any stenosis or abnormality found.
Most catheterization laboratories are “single plane” facilities, those that have a single X-ray generator source and an x-ray image intensifier for fluoroscopic imaging. Older cath labs used cine film to record the information obtained, but since 2000, most new facilities are digital. The latest digital cath labs are biplane (have two X-ray sources) and use flat panel detectors.
Cardiac catheterization laboratories (or Cath Lab) are usually staffed by a multidisciplinary team. This may include a medical practitioner (normally either a consultant cardiologist or radiologist), cardiac physiologist, radiographer and nurse.
Cardiac catheterization is a general term for a group of procedures that are performed in the cath lab, such as coronary angiography. Once a catheter is in place, it can be used to perform a number of procedures including angioplasty, PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention) angiography, transcatheter aortic valve replacement, balloon septostomy, and an electrophysiology study or catheter ablation. Devices such as pacemakers may be fitted, or rotablation to remove plaque can be performed.